WhatsApp:
+86 18866361895
WhatsApp:
+86 18866361895
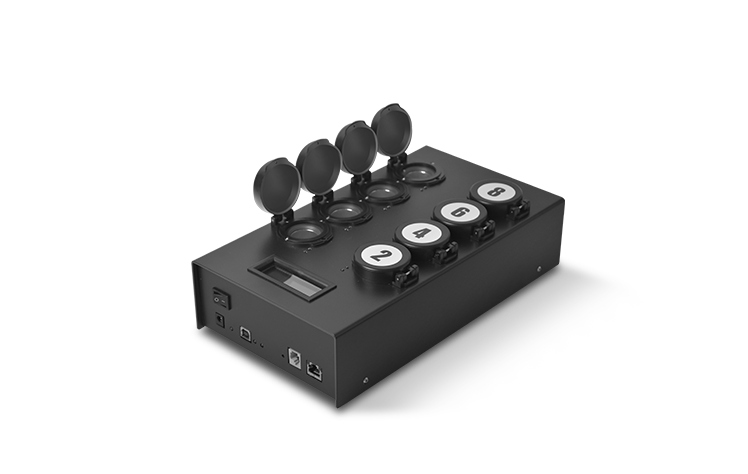


型号:YT-W80
MBS Microbial Rapid Detection System, imported from Italy. Based on the international cutting-edge MBS method patent detection technology from the University of Rome in Italy, it i···
WhatsApp:+86 18866361895(Manager Xu)
WeChat:+86 17865361250(Manager Xu)
Email:yuntang@foxmail.com
Technical Parameter
Picture Introduction
MBS Microbial Rapid Detection System, imported from Italy. Based on the international cutting-edge MBS method patent detection technology from the University of Rome in Italy, it integrates rapid cultivation and high-sensitivity innovative detection methods, greatly reducing detection time; Making complex microbial detection simple and easy to operate, without any pre-treatment, the fully enclosed detection system is safe and harmless, widely applicable to food and drug systems, food enterprises, daily chemical product manufacturing, medical and health, pharmaceutical research and manufacturing, environmental protection, and catering service enterprises.
1、 MBS Microbial Rapid Detection and Testing Items and Scope of Application
1.1 Testing items:
1. Testing items (including but not limited to): total bacterial count, coliforms, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Enterococcus, yeast, Enterobacteriaceae and other microorganisms.
2. Sample detection: can detect solid, liquid, surface, paste, and slurry samples.
3. Inspection speed: 2-5 times faster than traditional inspection methods. The detection can be completed and a quantitative analysis report can be issued within 2.5 hours at the fastest (when the concentration of Escherichia coli in the tested sample is greater than 107 CFU/ml)
1.2. Scope of Application
1. Food: meat, fruits and vegetables, dairy products, staple foods, seasonings, beverages, semi processed foods and beverages, agricultural products and related processing companies;
2. Water quality: domestic drinking water, natural water sources, and water treatment plants;
3. Surface: Clean table, tableware/utensil surface;
4. Others: drugs, cosmetics, etc;
5. HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) diagnosis, as well as rapid microbiological safety testing applicable to disaster sites, on-site inspections, sampling, large-scale conferences, and other locations.
2、 Composition of MBS Microbial Rapid Detection System
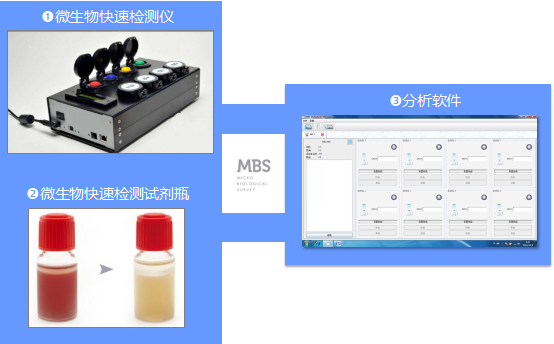
3、 Working principle
The MBS method for microbial detection uses a reagent bottle containing redox dye as the initial medium to measure the redox state. When microorganisms are present, the redox state of the detection reagent bottle will be altered, resulting in a color change of the redox dye.
2. The time required for color change in MBS method for microbial detection is inversely proportional to the microbial content in the sample, that is, the more microorganisms there are, the shorter the time required for color change; The lower the microbial content, the longer the time required for color change. If the target microorganism does not exist, there will be no color change in the reagent.
3. Qualitative analysis: The change in reagent color can be observed visually. After adding the sample, place the reagent bottle in a constant temperature chamber with a set temperature, and observe the color change visually at different time points. If the reagent bottle changes from a negative color to a positive color, microorganisms are present.
4. Semi quantitative analysis: Based on the time required for the color change of the reagent bottle (negative color to positive color), refer to the control table (comparison table of the relationship between the color change time of the reagent bottle and the microbial content) to roughly determine the amount of microorganisms present.
5. Accurate quantitative analysis: Color changes can also be detected by MBS microbial rapid detection instrument. After adding the sample, place the reagent bottle into the detector, select the target microorganism to be detected, and the detector will automatically adjust the incubation temperature. Each detection well position will be independently controlled for temperature and independent detection, and the microbial content in the sample will be directly obtained.
4、 Testing process and steps
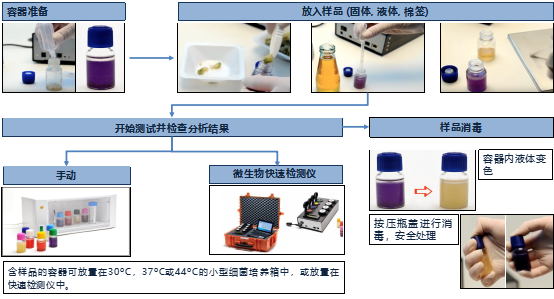

Easy to operate: The sample does not require any pre-treatment or bacterial culture, and can be directly added and analyzed automatically. Non professionals can also operate it. Just dissolve the reagent, add the sample, put it into the instrument, and click to start the test. With just four steps, a detection report can be automatically generated, without the need for tedious steps such as UV light irradiation, cultivation, and manual reading.
5、 MBS Usage Instructions
1. Each microbial rapid detection reagent bottle detects different microorganisms, and the reagent bottle contains oxidoreductases specific to certain microbial classes. When a sample contaminated with microorganisms is inserted into a reagent bottle, the oxidoreductase will undergo a chemical reaction, causing a change in the color of the liquid in the bottle. The color of the liquid will change according to the number of microorganisms in the bottle.
2. Reagent bottles containing samples can be placed in small bacterial incubators at 30 º C, 37 º C, or 44 º C, or in MBS microbial rapid detection devices for testing
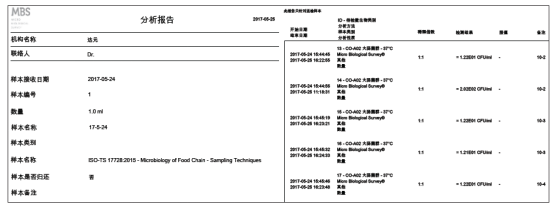
3. MBS microbial rapid detector can independently detect 8 reagent bottles (8 different bacterial samples) simultaneously, control the temperature separately, and provide quantitative analysis reports separately. The analysis report is read through separately installed software, which is suitable for systems including Windows XP and Vista
4. After use, press the container mouth to add the chlorine based solution into the container for sterilization. The microorganisms in the container can be killed within a few minutes to achieve the purpose of disinfection.
6、 Technical parameters
1. Sensitivity: 1 CFU/ml (g) (1 live bacterium).
2. Range: 1 CFU/ml (g)~9 × 109 CFU/ml (g)
3. Specificity: ≥ 99.999% (theoretical extreme value).
4. Sample size: 1.0ml or 1.0g
5. Software compatible with operating systems: Windows XP, Vista, 7/8/10
6. Size: ≤ 31x17,5x8 cm (W x L x H)+adapter
7. Weight: ≤ 1.9kg
7、 Features and advantages:
1) Sample well positions: ≥ 8, each detection well position has independent temperature control and incubation capabilities, and can simultaneously perform microbial detection at different cultivation temperatures. The target detection strain can be selected arbitrarily. After completing the detection at a certain detection position, the next detection can be started immediately without waiting for other samples in the batch to complete the detection
2) Photodetector: A matrix chip composed of three photodiodes, each with a different color filter, and a filter placed on top of the photodetector to reduce near-infrared radiation
3) Data management: Test result documents can be directly exported in PDF or other formats
4) The sample does not require any pre-treatment or bacterial culture, and can be directly added for testing. Non professionals can also operate it, making it suitable for use in testing vehicles and grassroots units
5) After testing, there is no need to open the lid. After pressing the bottle cap, sterilization is completed in one step without environmental or personnel contamination risks, and no other sterilization equipment is required
6) The accuracy of the test results is not affected by factors such as pH value, color, and turbidity
7) Both indicator bacteria and pathogenic bacteria detection can be carried out using qualitative or quantitative methods
8) Fully automatic analysis: automatically stops upon completion of detection, compatible with different computer operating environments and databases
9) All detection traces can be tracked and queried through the built-in chip
10) The instrument can be directly controlled by a computer for testing
8、 Advantages of MBS Microbial Rapid Detection System
1. The MBS microbial rapid detection system can perform microbial analysis on solids, liquids, food, water (drinking water, surface water, wastewater, industrial water, etc.), and object surfaces using only one container, saving technology, cost, and time
2. Fast speed: No preprocessing required, 2 to 5 times faster than traditional methods;
3. Easy to use: Anyone can analyze without any reagents or instruments, and on-site testing is possible without the need for a laboratory environment;
4. Strong sensitivity: It can analyze any individual cell in the sample with a specificity of 99.999%;
5. Wide applicability: can analyze 99.9% of bacterial species in samples;
6. Low cost: 2 to 4 times cheaper than traditional analysis methods;
| MBS | 培养法 | ATP | 生化法 | 基因法 | 免疫法 | |
| 灵敏度 | 优 | 优 | 不差 | 弱 | 优 | 不差 |
| 专一性 | 不差 | 不差 | 弱 | 不差 | 优 | 优 |
| 灵活性 | 优 | 优 | 优 | 弱 | 弱 | 弱 |
| 可定量 | 优 | 优 | 不差 | 弱 | 不差 | 不差 |
| 检测速度 | 不差 | 弱 | 优 | 不差 | 优 | 优 |
| 简便性 | 优 | 优 | 不差 | 优 | 弱 | 弱 |
| 自动化 | 优 | 不差 | 优 | 不差 | 不差 | 不差 |
| 无预处理 | 优 | 弱 | 弱 | 弱 | 弱 | 弱 |
| 无害处理 | 优 | 弱 | 弱 | 弱 | 弱 | 弱 |
MBS Microbial Rapid Diagnosis Q&A
Can microbiological testing bottles detect dead bacteria in addition to live ones?
Answer: Cannot detect dead bacteria.
Can microbial detection bottles detect anaerobic bacteria?
Answer: The detection range of the test bottle includes both anaerobic bacteria (such as Clostridium sulfite reducing Clostridia and Clostridium perfringens) and aerobic bacteria.
The reagents used in the detection bottles for detecting different types of microorganisms are different. For anaerobic bacteria, we have special reagents, such as detecting Clostridium perfringens.
3. What detection methods are used for the detection principles of bottles?
Answer: Culture dish method, enzyme method, immune method, gene method.
Can you briefly describe the advantages and disadvantages of these methods for question 3?
Answer: Unlike traditional methods such as culture medium, colloidal gold, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and PCR, the German Royal Microbial Detector is a collection of multiple methods. Using a single detection method has its own drawbacks: for example,
PCR method requires professional technicians and expensive equipment;
The operation of the cultivation medium method is complex;
The colloidal gold method has low sensitivity;
Insufficient specific capture by enzyme immunoassay.
The German Royal Microbial Detection Bottle Rapid Detection Series products are a comprehensive application of multiple methods mentioned above, absorbing the advantages of each method and making up for the shortcomings of various methods.
When using a microbiological testing bottle for microbiological testing, should the sample or sterile water be placed first?
Answer: Either is possible.
6. Is it necessary to inoculate the sample with microorganisms in a sterile environment?
Answer: The detection bottle is analyzed by capturing specificity and combining multiple detection methods. Whether it is a sterile environment or not is acceptable (most of the testing sites are non sterile environments).
Can the detection bottle detect surface samples and solid samples?
Answer: Solid, liquid, and surface samples can be tested (by wetting the surface with sterile water using the provided cotton swab). Pulp and other paste like, paste like, and viscous substances can all be detected.
8. Do detection bottles need to undergo pre-treatment processes such as grinding and dilution when detecting solid samples?
Answer: Put the sample directly into the testing bottle without any pre-treatment.
What is the amount of sterile water used for each test?
Answer: Generally, it is 11ml. If testing liquid or water samples, it is recommended to add 1ml of sample and 10ml of sterile water.
10. After adding the sample and sterile water, is the step of "shaking well to fully dissolve and mix" necessary for both qualitative and quantitative analysis?
Answer: Yes, shaking well is a necessary step for both qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Is the incubation temperature the same for different microorganisms? Please provide examples to illustrate.
Answer: It's different. Most of them are at 37 degrees Celsius: total number of live bacteria, Salmonella, Listeria, etc., Escherichia coli at 44 degrees Celsius, etc. Please refer to the comparison table for details.
12. If testing samples such as cold dishes or ice cream, should incubation be carried out at low temperatures?
Answer: There is no limit on the temperature of the test sample itself. For microorganisms in the test sample, please strictly follow the incubation temperature corresponding to the microorganisms being tested, and still refer to the control table.
13. If you want to speed up the detection time, can the incubation temperature be adjusted to be higher than the incubation temperature corresponding to the detected microorganisms?
Answer: No, strictly follow the comparison table.
What is the sample size specified in the operation manual?
Answer: 0.1g-1.0g or 0.1ml-1.0ml.
If the sample size is higher than the specified sample size, will the test results be different, or will the test results (when quantifying) increase?
Answer: If the sample size is larger or smaller, the quantitative analysis results will not change.
Reason: Traditional microbiological testing methods, including reference methods such as colony counting based on solid selective culture media, have inherent statistical dispersion (statistical term, also known as statistical variation, is the spread of variables or probability distributions, common examples being variance, standard deviation, and interquartile range) greater than 50%. Many laboratories have confirmed that the Royal Biological Testing method has lower statistical dispersion and higher reliability compared to other testing methods. However, regardless, there is still a statistical dispersion of 25-30%. In addition, the statistical dispersion generated by sampling should also be considered
Solid meat products, especially those that are prone to microbial growth.
Therefore, the results obtained by adding 0.5g or 1.5g of sample are statistically equivalent (equivalent to the results obtained by any other method).
Can low-density bulk samples such as flour be tested as usual?
Answer: Sure.
17. Will dark samples like soy sauce affect the interpretation of qualitative testing results? Do you have any good suggestions?
Answer: If paired with a detector for quantitative analysis, there is no such problem; If qualitative analysis is only based on visual observation of discoloration, it is recommended to dilute dark samples before testing if there is concern that they may not be clearly recognizable by the naked eye. Do you remember the answer to question 15? The results obtained by adding 0.5g or 1.5g are statistically equivalent to those obtained by any other method. The same principle applies to dilution.
18. If testing water samples, do we still need to add sterile water? How much to add?
Answer: It is recommended to add 1ml of water sample and 10ml of sterile water.
Are the starting colors and positive colors corresponding to different microorganisms the same? Please provide examples to illustrate.
Answer: Different.
For example, the initial color of Salmonella after incubation for about 10 minutes is red, and the positive color is yellow; Listeria monocytogenes starts with a blue color and a positive color is yellow. Please refer to the comparison table for details.
Does the microbial detector also have the function of an incubation machine?
Answer: Yes. Shake the detection bottle thoroughly and immediately put it into the detector. After setting the detection bacteria on the software.
The detector will automatically incubate and provide a quantitative analysis report.
Does the microbial detector also have the function of an oscillator?
Answer: Not available. Shake vigorously by hand for 2-3 minutes, or shake the shaker for about 20 seconds until fully dissolved or mixed.
What is the reading principle of a microbiological detector?
Answer: Microbial detector is a precision optical reading instrument. Accurately detect color changes in the bottle through optical principles and provide precise quantitative analysis and detection reports.
Is the microbiological detector powered by an external source or comes with a rechargeable battery?
Answer: External power supply.
24. How many detection bottles can the microbial detector detect simultaneously and independently?
Answer: 8. Simultaneously, independently detect and provide quantitative analysis reports separately.
25. Do I need to install analysis software on a computer for quantitative analysis with a microbial detector?
Answer: It is necessary to follow the supporting analysis software.
26. What computer operating system is compatible with the analysis software?
Answer: XP, Vista, Windows 7
27. If the detector is powered on for the first time, how long does it take to wait before proceeding to the next step after connecting the power?
Answer: If you are starting up for the first time, it is advisable to stay for about 40 seconds after starting up and continue operating.
When using a detector for quantitative analysis, should the fully mixed detection bottle be immediately placed in the detector or wait for a moment before placing it in?
Answer: After thorough mixing, immediately put it into the detector.
After placing the detection bottle into the detector, click on "Start" in the analysis software of the detector. What color will the corresponding detection hole light on the software interface turn into?
Answer: Click "Start" on the corresponding operation interface of the detected bottle, and the indicator light of the corresponding hole will change from green to red. Indicates that the detection has started and is in progress.
30. After the detection is completed, what color will the light on the corresponding hole in the analysis software interface restore, indicating that the detection is complete and a new sample can be placed?
Answer: During the inspection, the indicator light is red. After the detection is completed, the indicator light turns green. At this point, it is possible to place a new detection bottle into the corresponding detection hole of the detector to start the next round of testing. The detection time is determined by the presence of bacteria (when the microbial content is high), or by the detection time corresponding to the control table (when the microbial content is low, it should exceed the detection time corresponding to 1 CFU in the control table).
What is the relationship between the analysis time of microbial detection bottles and the microbial content in the detection bottles?
Answer: There is an inverse relationship. The higher the microbial content, the shorter the corresponding detection time; The lower the microbial content, the longer the corresponding detection time. If the microbial content in the sample is too high, the quantitative analysis results of the detector will significantly change within minutes or even seconds; If the microbial content is very low (due to RVLM being a very precise and sensitive instrument), experienced use can preliminarily determine whether the target microbial content meets the specified requirements through changes in data over several hours or even minutes.
32. Before analyzing and testing, should there be a clear experimental purpose to determine the microbial content you want to test (according to national standards for the amount of microorganisms present)?
Answer: That's right.
For example, according to national GB standards or international EC standards, there are clear (or partially clear) indications of the allowable levels of microorganisms in different poultry and livestock species.
Specifically, when conducting microbiological testing, we must first clarify the purpose of the test. As stipulated in the international EC 2073:2005 standard, the allowable amount of Escherichia coli in fresh meat is CFU 10 ^ 2/g, which means that the content of Escherichia coli in each gram of fresh meat cannot exceed CFU 10 ^ 2. At this point, based on the recruitment table, we find the column where Escherichia coli is located and check the log CFU 10 ^ 2=2, which means that the number 2 in the Escherichia coli row corresponds to the column with the number 14. Whether it is qualitative analysis with the naked eye or quantitative analysis with a detector, to detect whether the content of Escherichia coli in the sample exceeds CFU 10 ^ 2, strict and accurate analysis results can be obtained within a maximum of 14 hours.
If quantitative analysis is conducted on the detection bottle, experienced experimenters will make a preliminary judgment on the microbial content in the detection bottle based on the dynamic changes in quantitative analysis data within a short period of time (such as ten minutes).
What is the purpose of clearly detecting microbial content and what is the role of the reference table?
Answer: It is the basis for determining the incubation temperature, starting color, analysis time, and positive color standard control corresponding to the detected microorganisms. Please refer to the answer to the previous question for specific usage methods.
34. What is CFU?
Answer: Colony forming unit.
The abbreviation for the unit of formation of bacterial clusters obtained through cultivation.
The unit of measurement for bacteria (visible) and fungi. CFU:colony‐forming unit, Colony forming unit refers to the process of diluting a certain amount of bacterial liquid by pouring or coating, allowing the individual microbial cells inside to disperse one by one on an agar plate. After cultivation, each living cell forms a colony. Unlike the conventional measurement of microbial count using a microscope, it is mainly a unit for measuring the number of visible (i.e., in most cases, forming colonies) bacteria. The meaning is how many single cells are contained in each milliliter of bacterial liquid! Traditionally, it is called 'one'. However, we know that a colony is not necessarily generated by a single bacterium, but may also be generated by a cluster of bacteria (a cluster of bacteria). In this case, it is not very accurate to call it "individual". The accurate name is "colony forming unit", abbreviated as "CFU" in English. Just like "kilogram" and "kilogram", they are just called differently, but there is no change in quantity.
CFU stands for 'colony forming units'. CFU/mL refers to the total number of bacterial communities contained in each milliliter of sample, and CFU/g is also used to correspond to solid culture medium.
If I want to test the bacterial count of Escherichia coli in the sample, it should not exceed 106 CFU/g or 106 CFU/ml,
Observe the color changes in the bottle with the naked eye for qualitative analysis. Please refer to the "Incubation Temperature and Color Comparison Table" to describe the testing steps in detail.
Answer: Step: Put in the sample
Add the sample to be tested (0.1-1.0g, or 0.1-1.0ml), add 11ml of sterile water (depending on the condition of the test substance, if it is a liquid, it is recommended to add 1ml of sample and 10ml of sterile water. The difference is not significant), and close the bottle cap tightly.
Step 2: Shake the bottle until the solvent is fully dissolved or mixed.
If you need to shake vigorously with your hands for about 2-3 minutes; Or shake with an oscillator, which takes about 20 seconds.
Step 3: Read the test results at the appropriate time
(1) If qualitatively analyzed with the naked eye. Determine the incubation temperature, starting color, detection time, positive color, and other information corresponding to the Escherichia coli population based on the reference table.
Incubation temperature: 37 ℃ according to the control table;
Starting color: The color that will appear after shaking well and incubating at 37 ℃ for about 10 minutes. According to the comparison table, it is red;
Testing time: The standard for testing is that the coliform group content should not exceed 106 CFU/g or 106 CFU/ml. According to the comparison table, the corresponding column is log 106=6, and the number in the row corresponding to the number 6 is 6, which means the detection time is 6 hours. That is, the observation time is determined to be 6 hours.
Positive color: According to the control table, the positive color for Escherichia coli is yellow.
After confirming the following information, we placed the fully mixed detection bottle in a 37 ℃ constant temperature chamber and kept it there. After incubating for about 10 minutes, we will observe that the detection bottle will display the starting color corresponding to the detection of coliforms - red. Continue to place and observe for 6 hours. If the color turns yellow, it indicates that the coliform bacteria content in the sample exceeds 106 CFU/g or 106 CFU/ml, and the sample is considered unqualified; If the sample does not turn yellow but maintains its initial color of red or other intermediate colors, it indicates that the coliform bacteria content in the sample does not exceed 106 CFU/g or 106 CFU/ml, and the sample is qualified.
(2) If the detector performs quantitative analysis
Please refer to the next question for this step.
Step 4: Aseptic treatment
Finally, don't forget to sterilize the test bottle by pressing the top of the bottle cap. After pressing the bottle cap and shaking it, it is safe to discard.
Attention: When conducting experimental operations, do not touch the top of the cap of the test bottle to avoid improper aseptic treatment, which may affect the test results.
If the 34th question is paired with a detector for precise quantitative analysis, please provide detailed steps for the operation.
Answer: (2) If the detector performs quantitative analysis
Immediately place the fully mixed detection bottle into the detector.
Start the detector software, click on "Station" (status) to enter relevant information (including: inspector name, testing, customer to which the test sample belongs, testing time, etc.); Select the microbial species to be detected from the dropdown menu of "analysis type" in the software operation interface, click OK, click Start, and the indicator light will turn red,
Start entering the analysis state. Observe the quantitative analysis data changes of the detector and make judgments.
Why can't the cap of the test bottle be pressed before the end of the test?
Answer: Aseptic treatment. There are sterile substances in the bottle cap. Pressing the cap will allow the sterile substances in the cap to enter the bottle and react with the solvent inside, completing the sterile treatment. Therefore, please do not easily touch the cap of the detection bottle during the experiment.
Technicians are required to answer the following questions:
How many types of microorganisms can be detected by the detection bottle, and what are they?
Answer: Total number of live bacteria, coliforms, Escherichia coli, Enterobacteriaceae, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, Enterococcus, Clostridium perfringens, Aspergillus, Aspergillus, yeast.
In the future, detection bottles for other microbial strains will be released one after another. Including Legionella bacteria, etc.
Can the detection bottle detect all strains of Escherichia coli (including the currently popular EHEC) when detecting Escherichia coli? )
Answer: Yes, all strains of Escherichia coli, including EHEC enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (E. coli O104, O111, O157, etc.), can be detected
What are the application scope of the detection bottle?
Answer: Hygiene control: Food (HACCP), kitchen, tools, surfaces (HACCP), water quality, disease control (CDC), import and export inspection and quarantine, drugs and cosmetics.
Related to our daily lives: environmental monitoring agencies, agricultural products and related processing companies, water source testing and treatment plants, water distribution companies, pharmaceutical factories, pharmacies, cosmetics factories, analytical laboratories and HACCP diagnostics, dairy factories, cafes, restaurants, consumer protection groups, business management agencies, indoor air conditioning regulation companies, especially suitable for rapid food testing in military and large-scale exhibitions.
Do you think that E. coli testing bottles, Listeria testing bottles, and Salmonella testing bottles are suitable for medical purposes besides being used for food safety testing?
Answer: The three detection bottles for Escherichia coli (EHEC), Listeria monocytogenes, and Salmonella can be used for in vitro clinical testing.
The global positioning of the Royal microbiological testing bottle series remains food safety. In Europe, clinical in vitro testing of human microbiota is very rare, and various aspects of safety control in Europe are well regulated. However, in developing countries, in vitro clinical testing of the three microorganisms mentioned above often occurs. The safety and accuracy of the above three detection bottles for in vitro clinical testing can be guaranteed.
The difference in market positioning between 4-in-1 test strips and detection bottles
1) Comparison between 4-in-1 test strips and detection bottles
When combined with its analyzer, a 4-in-1 test strip can simultaneously detect 48 test strips. Therefore, from the perspective of economic cost, 48 pieces are checked simultaneously upon startup. For hospitals, once 48 fecal samples are collected, they will be analyzed in one go.
Testing bottle, one sample can be used for inspection. And the bigger advantage is that this product will be very popular among doctors. Because doctors do not need to come into contact with samples, which is currently impossible for most hospital tests to achieve. Give the bottle to the patient and let them put in the stool sample themselves before sending it back to the doctor. The doctor takes the test bottle, shakes it evenly on the hospital's shaker, and places it in the incubator, waiting for the results to be interpreted.
2) Comparison between testing bottles and traditional testing methods currently used in hospitals
At present, the testing method in hospitals is still mostly the culture dish method. The most frustrating aspect of this method for doctors is that they have to come into contact with the sample. If a doctor is pregnant, the consequence of exposure to Listeria monocytogenes is miscarriage. If the testing station is not cleaned thoroughly, it can also easily lead to the spread of microorganisms.
Testing bottles, doctors do not need to touch the samples at all. The process of placing the sample into the testing bottle can be left to the patient to operate in the bathroom. What doctors need to do is simply shake well and incubate in an incubator (both oscillators and incubators are standard equipment in hospitals).
5. Whether it is solid, liquid, or surface samples, do they not require pre-treatment during testing?
Answer: Yes
What is the specificity of the detector?
Answer: 99.999% (theoretical limit value)
What is the sensitivity of the detector?
Answer: The theoretical limit value for detecting one live bacterium can be reached.
How many steps are required for qualitative analysis and what are they?
Answer: Three steps: sample addition; Shake the bottle until fully dissolved and mixed; Read the results at the appropriate time (according to the comparison table). Finally, don't forget to press the top of the bottle cap for aseptic treatment.
How many steps are required for quantitative analysis and what are they?
Answer: Same as above. Please refer to the operation manual of the detector for details.
What is the purpose of pressing the cap of the test bottle after testing?
Answer: Aseptic treatment, please refer to question 45 above.
What is the storage temperature of the detection bottle?
Answer: It can be stored at around 20 ℃ -25 ℃, which is convenient for transportation and beneficial for temporary inspection. But with the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere, it is still important to pay attention to the storage temperature not exceeding 25 ℃ during summer, as this will affect the sensitivity of the detection bottle. However, if stored at 4 ℃, the shelf life can be extended by nearly twice.
